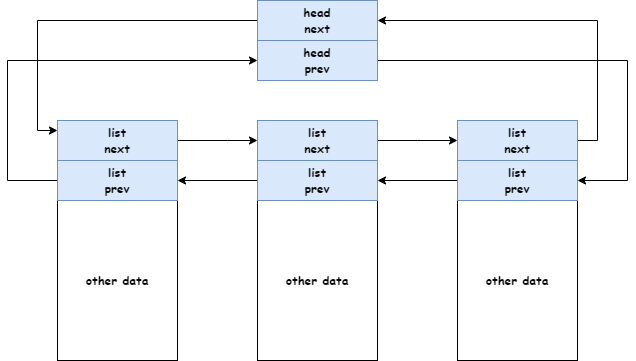
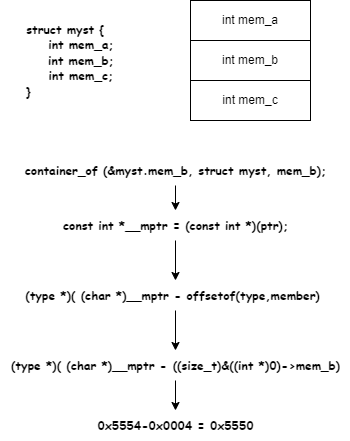
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
| #include "list.h"
#include <stdio.h>
struct example {
list_node list;
int value;
};
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
list_head head;
init_list_head(&head);
struct example e1, e2, e3;
e1.value = 1;
e2.value = 2;
e3.value = 3;
fprintf(stdout, "list_add_head: %d %d %d\n", e1.value, e2.value, e3.value);
list_add_head(&e1.list, &head);
list_add_head(&e2.list, &head);
list_add_head(&e3.list, &head);
struct example e4, e5, e6;
e4.value = 4;
e5.value = 5;
e6.value = 6;
fprintf(stdout, "list_add_tail: %d %d %d\n", e4.value, e5.value, e6.value);
list_add_tail(&e4.list, &head);
list_add_tail(&e5.list, &head);
list_add_tail(&e6.list, &head);
struct example *pos;
list_for_each_entry(pos, &head, list)
{
fprintf(stdout, "value: %d\n", pos->value);
}
fprintf(stdout, "list_del %d\n", e2.value);
list_del(&e2.list);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &head, list)
{
fprintf(stdout, "value: %d\n", pos->value);
}
fprintf(stdout, "list_add_prev list_add_next: in = %d cur = 5\n", e2.value);
struct example *next, *cur;
list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, next, &head, list)
{
if (pos->value == 5)
{
cur = pos;
break;
}
}
struct example e7, e8;
e7.value = 7;
e8.value = 8;
fprintf(stdout, "prev in = %d cur = %d\n", e7.value, cur->value);
list_add_prev(&e7.list, &cur->list);
fprintf(stdout, "next in = %d cur = %d\n", e8.value, cur->value);
list_add_next(&e8.list, &cur->list);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &head, list)
{
fprintf(stdout, "value: %d\n", pos->value);
}
fprintf(stdout, "list_del all\n");
list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, next, &head, list)
{
fprintf(stdout, "del value: %d\n", pos->value);
list_del(&pos->list);
}
if (list_empty(&head))
{
fprintf(stdout, "list is empty\n");
}
return 0;
}
|